
On This Page
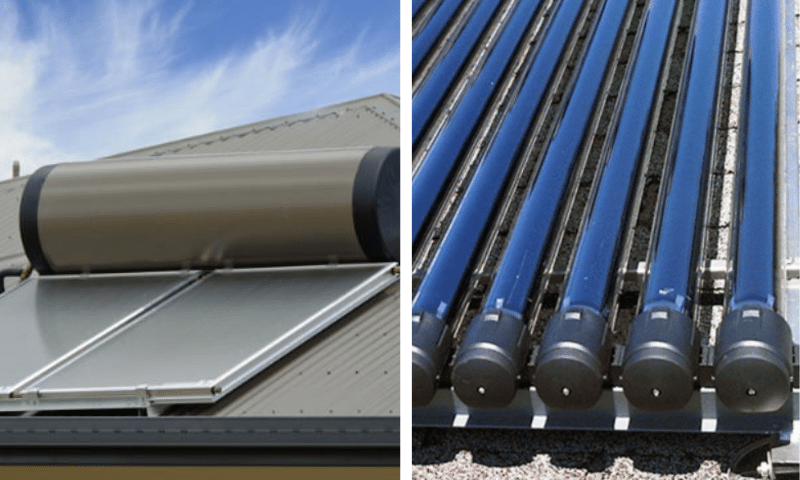
Solar hot water has come a long way in the last decade. This is particularly so with the introduction of evacuated tube collectors that are rapidly becoming the preferred option over flat plate systems.
Difference between flat plate collector and evacuated tube collector
Flat plate collectors and evacuated tube collectors are two commonly used types of solar thermal collectors in Australia. The main difference between these two types lies in their design and efficiency.
Flat plate collectors are the simpler of the two, consisting of a flat, rectangular panel coated with a heat-absorbing material and covered by a glass or plastic sheet. They are relatively easy to install and maintain, making them a popular choice for residential and small-scale applications.
Energy Matters has been a leader in the renewable energy industry since 2005 and has helped over 40,000 Australian households in their journey to energy independence.
Let us discuss and choose the best quote that suits your needs and budget, and we can connect you with our trusted local solar installers in Melbourne, who will provide up to 3 FREE quotes for your home and business solar energy system. Get your free quotes today!
Evacuated tube solar hot water collectors
Evacuated tube solar hot water collectors comprise a series of cylindrical tubes, each containing a vacuum-sealed space.
The vacuum-sealed space acts as insulation, which helps to keep the heat inside the tube.
The outer layer of the tube is made of high-quality glass, which allows sunlight to pass through but does not allow heat to escape. The inner layer of the tube is coated with a special material that absorbs the sunlight and converts it into heat. The heat is then transferred to a fluid that circulates through the tubes and is stored in a hot water tank.
Due to their higher efficiency and performance, evacuated tube collectors are typically used in larger, commercial applications. However, they are also more expensive to install and maintain than flat plate collectors.
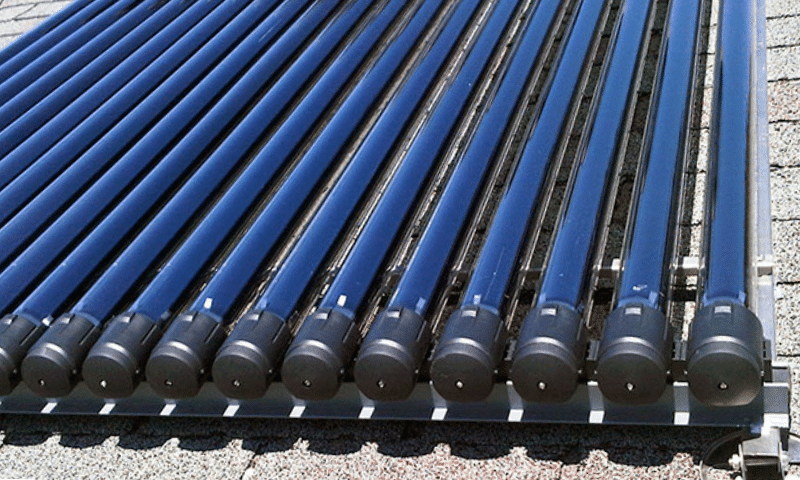

How does an evacuated tube solar hot water collector work?
An evacuated tube solar hot water collector works by capturing the sun’s energy and transferring it to a heat exchanger, which then heats the water. As the sun’s energy passes through the glass tube, it is absorbed by the heat pipe, which causes the liquid inside to boil and produce steam. The steam rises to the top of the tube, transferring its heat to a heat exchanger. The heat exchanger then transfers the heat to the water, which is then stored in a hot water tank until it is needed.
Advantages and challenges of evacuated tube solar hot water collectors
The use of evacuated tube solar hot water collectors have several advantages. Firstly, they are highly efficient, with an efficiency rating of up to 80%. This means that they can provide a significant amount of hot water using minimal amounts of sunlight. Secondly, they are low maintenance, requiring very little upkeep or repair. Thirdly, they are cost-effective, especially when compared to other forms of solar energy production.
Another advantage of evacuated tube solar hot water collectors is that they can be used in various settings, from residential homes to large commercial buildings. They can also be used in remote areas not connected to the electricity grid, providing an affordable and sustainable source of hot water.
Benefits of evacuated tube solar hot water collectors in Australia
Evacuated tube solar hot water collectors have several benefits, which include:
Efficiency: Evacuated tube solar hot water collectors are more efficient than flat plate solar collectors, especially in colder climates or when there is limited sunlight. The tubes can capture sunlight from multiple angles, ensuring maximum energy absorption.
Cost-effective: Using solar energy can significantly reduce energy costs, especially in Australia where electricity costs are high. Evacuated tube solar hot water collectors are inexpensive to install and require minimal maintenance, making them a cost-effective solution for homes and businesses.
Environmentally friendly: Evacuated tube solar hot water collectors do not produce emissions, making them an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional energy sources. Solar energy can help to reduce Australia’s carbon footprint and support efforts to combat climate change.
Reliable: Evacuated tube solar hot water collectors are reliable and require minimal maintenance. They can be used in various applications, including heating homes, and pools, and producing hot water for domestic use.
Long lifespan: Evacuated tube solar hot water collectors have a long lifespan and can last up to 25 years or more with minimal maintenance.
Despite the many advantages and benefits of evacuated tube solar hot water collectors, there are also some challenges to their use.
For example, in areas with high levels of cloud cover or low levels of sunlight, the collectors’ efficiency may be reduced. Additional heating sources may be required to supplement solar energy.
Flat plate collectors
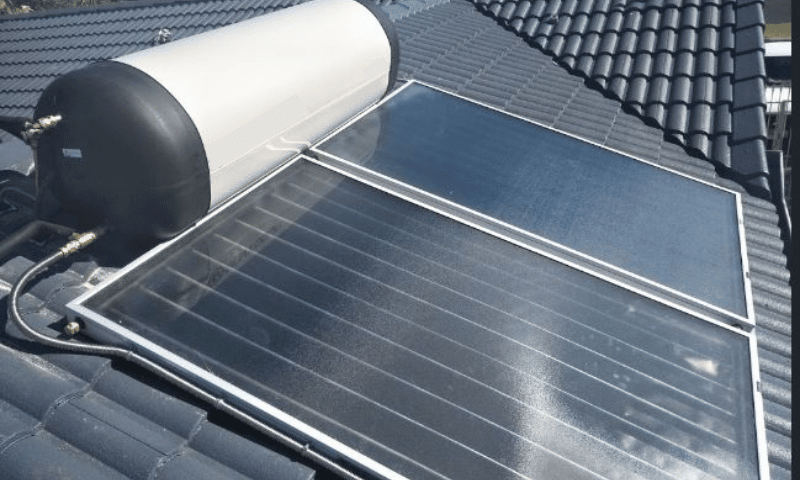
Flat plate collectors consist of a shallow rectangular box with a glass cover, insulation, and a dark-coloured absorber plate. The absorber plate is typically made of copper or aluminium, and it is coated with a special material that absorbs sunlight and converts it into heat. The heat is then transferred to a fluid that circulates through tubes in the collector and carries it to a storage tank, which can be used for hot water, space heating, or other applications.
In Australia, flat plate collectors are commonly used for domestic hot water systems, as well as for heating swimming pools and other outdoor recreational areas. They are also used in commercial and industrial applications, such as food processing and agricultural operations, where hot water or steam is required.
How does a flat plate collector work?
A flat plate collector uses the sun’s energy to heat a fluid, usually water or a mixture of water and antifreeze, which circulates through pipes in the collector. As the fluid circulates through the collector, it absorbs the heat from the absorber plate and carries it away to be used for various applications such as heating homes, and pools, or producing hot water for domestic use.
The fluid is heated by absorbing the sun’s radiation, which passes through the cover plate and is absorbed by the absorber plate. The absorber plate is designed to maximise the absorption of sunlight by using a dark-coloured metal with a high heat-absorbing capacity.
As the fluid heats up, it is then transferred to a storage tank where it can be used for various applications.
Advantages and challenges of flat plate collectors
One of the advantages of flat plate collectors is their relatively low cost compared to other solar thermal technologies. They are also easy to install and maintain, and they have a long lifespan, typically lasting 20-30 years. In addition, they are highly efficient, with a typical efficiency rating of around 70-80%.
Benefits of flat plate solar collectors in Australia
Flat plate solar collectors have several benefits, which include:
Cost-effective: The use of solar energy can significantly reduce energy costs, especially in Australia where electricity costs are high. Flat plate solar collectors are inexpensive to install and require minimal maintenance, making them a cost-effective solution for homes and businesses.
Environmentally friendly: Flat plate solar collectors do not produce any emissions, making them an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional energy sources. The use of solar energy can help to reduce Australia’s carbon footprint and support efforts to combat climate change.
Reliable: Flat plate solar collectors are reliable and require minimal maintenance. They can be used in various applications, including heating homes, and pools, and producing hot water for domestic use.
Long lifespan: Flat plate solar collectors have a long lifespan and can last up to 25 years or more with minimal maintenance.
However, there are some challenges to using flat plate collectors, particularly in areas with high levels of cloud cover or low levels of sunlight. In these areas, the collectors’ efficiency may be reduced, and additional heating sources may be required to supplement the solar energy.
Despite these challenges, the use of flat plate collectors is growing rapidly. The country has abundant solar resources, and the government has implemented a range of incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies. In addition, many households and businesses are motivated to reduce their energy costs and carbon footprint, and flat plate collectors offer an effective and affordable solution.
Check out our page to learn more about solar hot water systems.
Flat plate vs evacuated tube - which is better?
The latest is certainly not always the greatest, so which is actually better – a flat plate solar hot water system or one that uses evacuated tube collectors? While evacuated tube technology is more of an investment, the benefits certainly outweigh the cost. Any additional cost may also be offset by solar hot water rebates!
Evacuated tube collector based systems:
- Capture sunlight better as they have a greater surface area exposed to the sun at any time
- Are more efficient in transferring heat – up to 163% demonstrated in Australian conditions!
- Can work in subzero temperatures
- Are durable and if a tube breaks, it can be easily and cheaply replaced.
- Provide excellent performance in overcast conditions
- Require a smaller roof area than comparable flat plate collectors
- Do not have the same level of corrosion problems as flat plate collectors
Solar hot water collectors efficiency comparisons
The results below speak for themselves on the improved efficiency of evacuated tube technology over flat plate collector solar hot water systems.
The following figures demonstrate the efficiencies of collectors when heating water from ambient temperature to 75 degrees Celsius – data provided by Hills Solar. Flate Plate Collector efficiency testing was performed at National Solar Test Facility Canada.
Sydney, New South Wales
Winter:
Based upon solar insolation of 426W/m2 and an ambient temperature of 13.1degrees Celsius in Sydney. Based on this, the Hills Esteem evacuated tube solar collector is on Average 104% more efficient per m2 of aperture compared to flat plate solar collector.**
Summer: Based upon solar insolation of 840W/m2 and an ambient temperature of 21.3 degrees Celsius in Sydney. Based on this, the Hills Esteem evacuated tube solar collector is on Average 50.5% more efficient per m2 of aperture.**
** Data taken from Hills Solar report on collector efficiencies – hills-collector-efficiency (380kb PDF)
Melbourne, Victoria
Winter:
Based upon solar insolation of 296W/m2 and an ambient temperature of 9.9 degrees Celsius in Melbourne. The Hills Esteem evacuated tube solar collector is on Average 163.5% more efficient per m2 of aperture over the flat plate solar collector.**
Summer: Based upon solar insolation of 861W/m2 and an ambient temperature of 19.8 degrees Celsius in Melbourne. The Hills Esteem evacuated tube solar collector is on average 51.5% more efficient..**
** Data taken from Hills Solar report on collector efficiencies – hills-collector-efficiency (380kb PDF)
Brisbane, Queensland
Winter:
Based upon solar insolation of 546W/m2 and an ambient temperature of 17.8 degrees Celsius in Brisbane. The Hills Esteem evacuated tube solar collector is on average 81% more efficient per m2 of aperture compared to the flat plate solar collector.**
Summer: Based upon solar insolation of 828W/m2 and an ambient temperature of 25.2 degrees Celsius in Brisbane. The Hills Esteem evacuated tube solar collector is on Average 54% more efficient.**
** Data taken from Hills Solar report on collector efficiencies – hills-collector-efficiency (380kb PDF)
Adelaide, South Australia
Winter:
Based upon solar insolation of 452W/m2 and an ambient temperature of 10.9 degrees Celsius in Adelaide. Based on this, the Hills Esteem evacuated tube solar collector is on Average 132% more efficient per m2 of aperture than the flat plate solar collector.**
Summer:
Based upon solar insolation of 953W/m2 and an ambient temperature of 22.1 degrees Celsius in Adelaide. Based on this, the Hills Esteem evacuated tube solar collector is on Average 52% more efficient.**
** Data taken from Hills Solar report on collector efficiencies – hills-collector-efficiency (380kb PDF)
A correctly installed solar hot water system can start saving you money straight away, while doing your bit towards a smaller carbon footprint.
Switching to a better plan?
You may already have an energy plan but want to shop for a better deal. If you’re looking to save money on your electricity and gas bills, Energy Matters can help using our “Energy Health Check”!
Energy Matters’ “Energy Health Check” is a cutting-edge energy comparator tool that allows you to compare your area’s most competitive retail offers. We collect the data from our wide range of trusted retailers, allowing you to decide about changing your plan.
If your goal is to minimise the cost of your gas and electricity bills, switch to a better plan now!




















































